Ebola is a severe and often fatal viral disease caused by the Ebolavirus. It was first identified in 1976 near the Ebola River in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (then Zaire), which is how it got its name.
There are several species of Ebolavirus, with the Zaire ebolavirus being the most deadly.
Key Points:
- Transmission:
- Ebola is transmitted to humans through contact with bodily fluids (such as blood, sweat, vomit, or feces) of infected animals or people.
- It is not airborne, but can spread through direct contact with contaminated surfaces or infected individuals.
- The initial transmission is thought to occur from fruit bats or other wildlife.
- Symptoms:
- Symptoms usually begin 2-21 days after exposure and include fever, severe headache, muscle pain, fatigue, vomiting, diarrhea, and unexplained bleeding or bruising.
- As the disease progresses, it can lead to organ failure, shock, and death.
- Outbreaks:
- The largest Ebola outbreak occurred in West Africa between 2014 and 2016, affecting Guinea, Liberia, and Sierra Leone. Over 11,000 people died during this epidemic.
- Smaller outbreaks have occurred in central and eastern Africa.
- Treatment:
- There is no specific antiviral treatment for Ebola, though supportive care (rehydration, maintaining oxygen levels, treating secondary infections) can improve survival.
- Vaccines have been developed, like the rVSV-ZEBOV vaccine, which has been shown to be highly effective in preventing Ebola.
- Experimental treatments, like monoclonal antibodies, have been used during outbreaks.
- Prevention:
- Avoiding contact with animals that may carry the virus and practicing safe burial techniques for victims are key preventive measures.
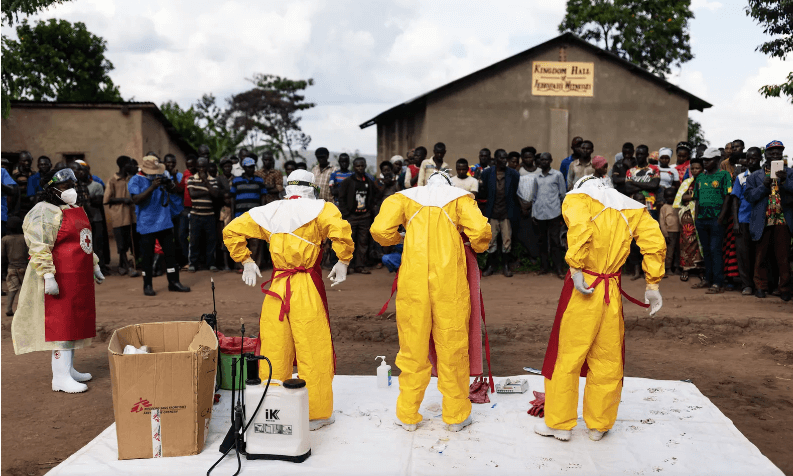
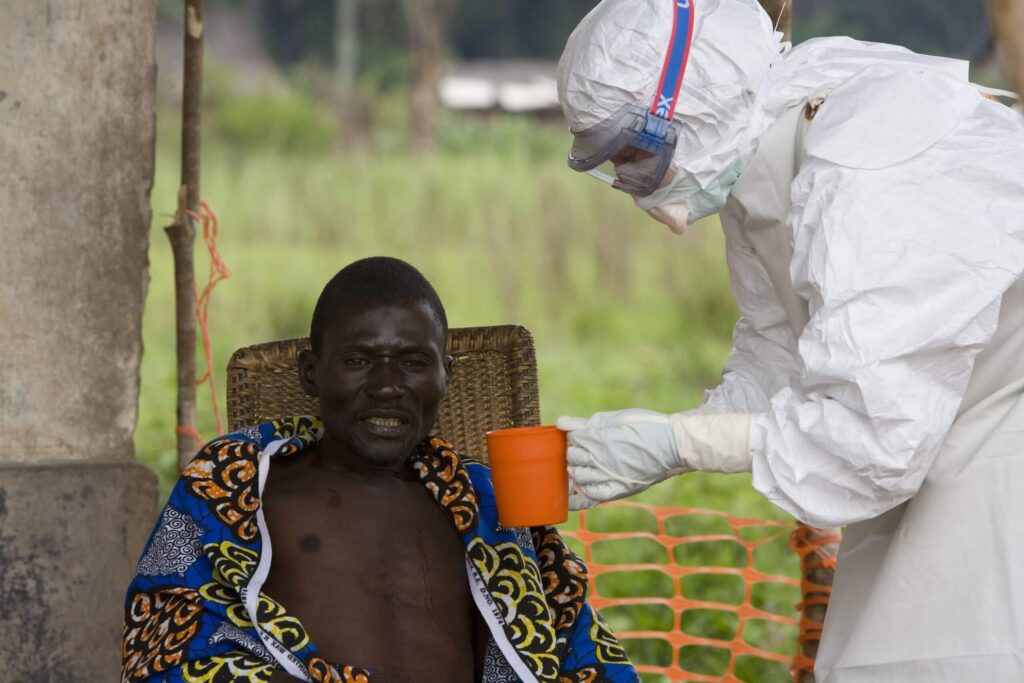
- Healthcare workers often face the highest risk and must use personal protective equipment (PPE) to avoid infection.
Ebola has a high fatality rate (50-90% in some cases), but early detection and appropriate medical care can greatly reduce mortality.
